Ham Extra License Practice Quiz
• Percentage: 0%; Correct: 0; Total: 0 of 50
E0A02: When evaluating RF exposure levels from your station at a neighbor's home, what must you do?
Make sure signals from your station are less than the controlled MPE limits
Make sure signals from your station are less than the uncontrolled MPE limits
You need only evaluate exposure levels on your own property
Advise your neighbors of the results of your tests
E1A01: When using a transceiver that displays the carrier frequency of phone signals, which of the following displayed frequencies represents the highest frequency at which a properly adjusted USB emission will be totally within the band?
The exact upper band edge
300 Hz below the upper band edge
1 kHz below the upper band edge
3 kHz below the upper band edge
E1B04: What must be done before placing an amateur station within an officially designated wilderness area or wildlife preserve, or an area listed in the National Register of Historical Places?
A proposal must be submitted to the National Park Service
A letter of intent must be filed with the National Audubon Society
An Environmental Assessment must be submitted to the FCC
A form FSD-15 must be submitted to the Department of the Interior
E1C04: When may an automatically controlled station retransmit third party communications?
Never
Only when transmitting RTTY or data emissions
When specifically agreed upon by the sending and receiving stations
When approved by the National Telecommunication and Information Administration
E1D10: Which amateur stations are eligible to be telecommand stations?
Any amateur station designated by NASA
Any amateur station so designated by the space station licensee, subject to the privileges of the class of operator license held by the control operator
Any amateur station so designated by the ITU
All of these choices are correct
E1E13: What are the consequences of failing to appear for re-administration of an examination when so directed by the FCC?
The licensee's license will be cancelled
The person may be fined or imprisoned
The licensee is disqualified from any future examination for an amateur operator license grant
All these choices are correct
E1F14: Under what circumstances might the FCC issue a "Special Temporary Authority" (STA) to an amateur station?
To provide for experimental amateur communications
To allow regular operation on Land Mobile channels
To provide additional spectrum for personal use
To provide temporary operation while awaiting normal licensing
E2A10: Why may the received signal from an amateur satellite exhibit a rapidly repeating fading effect?
Because the satellite is spinning
Because of ionospheric absorption
Because of the satellite's low orbital altitude
Because of the Doppler Effect
E2B17: What is the approximate bandwidth of a slow-scan TV signal?
600 Hz
3 kHz
2 MHz
6 MHz
E2C05: What is the function of a DX QSL Manager?
To allocate frequencies for DXpeditions
To handle the receiving and sending of confirmation cards for a DX station
To run a net to allow many stations to contact a rare DX station
To relay calls to and from a DX station
E2D07: Which of the following digital protocols is used by APRS?
PACTOR
802.11
AX.25
AMTOR
E2E11: What is the difference between direct FSK and audio FSK?
Direct FSK applies the data signal to the transmitter VFO
Audio FSK has a superior frequency response
Direct FSK uses a DC-coupled data connection
Audio FSK can be performed anywhere in the transmit chain
E3A05: Which of the following describes a method of establishing EME contacts?
Time synchronous transmissions with each station alternating
Storing and forwarding digital messages
Judging optimum transmission times by monitoring beacons from the Moon
High speed CW identification to avoid fading
E3B08: What type of HF propagation is probably occurring if radio signals travel along the terminator between daylight and darkness?
Transequatorial
Sporadic-E
Long-path
Gray-line
E3C13: What type of polarization is best for ground-wave propagation?
Vertical
Horizontal
Circular
Elliptical
E4A03: Which of the following parameters would a spectrum analyzer display on the vertical axis?
Amplitude
Duration
SWR
Q
E4B07: Which of the following is good practice when using an oscilloscope probe?
Keep the signal ground connection of the probe as short as possible
Never use a high impedance probe to measure a low impedance circuit
Never use a DC-coupled probe to measure an AC circuit
All of these choices are correct
E4C03: What is the term for the blocking of one FM phone signal by another, stronger FM phone signal?
Desensitization
Cross-modulation interference
Capture effect
Frequency discrimination
E4D11: Why are third-order intermodulation products created within a receiver of particular interest compared to other products?
The third-order product of two signals which are in the band of interest is also likely to be within the band
The third-order intercept is much higher than other orders
Third-order products are an indication of poor image rejection
Third-order intermodulation produces three products for every input signal within the band of interest
E4E05: How can noise from an electric motor be suppressed?
By installing a high pass filter in series with the motor's power leads
By installing a brute-force AC-line filter in series with the motor leads
By installing a bypass capacitor in series with the motor leads
By using a ground-fault current interrupter in the circuit used to power the motor
E5A11: What is the half-power bandwidth of a parallel resonant circuit that has a resonant frequency of 7.1 MHz and a Q of 150?
157.8 Hz
315.6 Hz
47.3 kHz
23.67 kHz
E5B13: What is the phase angle between the voltage across and the current through a series RLC circuit if XC is 250 ohms, R is 1 kilohm, and XL is 500 ohms?
81.47 degrees with the voltage lagging the current
81.47 degrees with the voltage leading the current
14.04 degrees with the voltage lagging the current
14.04 degrees with the voltage leading the current
E5C06: In polar coordinates, what is the impedance of a network consisting of a 100-ohm-reactance capacitor in series with a 100-ohm resistor?
121 ohms at an angle of -25 degrees
191 ohms at an angle of -85 degrees
161 ohms at an angle of -65 degrees
141 ohms at an angle of -45 degrees
E5D16: What is the power factor of an RL circuit having a 30 degree phase angle between the voltage and the current?
1.73
0.5
0.866
0.577
E6A04: What is the name given to an impurity atom that adds holes to a semiconductor crystal structure?
Insulator impurity
N-type impurity
Acceptor impurity
Donor impurity
E6B08: Which of the following describes a type of semiconductor diode?
Metal-semiconductor junction
Electrolytic rectifier
CMOS-field effect
Thermionic emission diode
E6C03: Which of the following describes tri-state logic?
Logic devices with 0, 1, and high impedance output states
Logic devices that utilize ternary math
Low power logic devices designed to operate at 3 volts
Proprietary logic devices manufactured by Tri-State Devices
E6D08: What is one important reason for using powdered-iron toroids rather than ferrite toroids in an inductor?
Powdered-iron toroids generally have greater initial permeability
Powdered-iron toroids generally maintain their characteristics at higher currents
Powdered-iron toroids generally require fewer turns to produce a given inductance value
Powdered-iron toroids have higher power handling capacity
E6E10: What is the equivalent circuit of a quartz crystal?
Motional capacitance, motional inductance and loss resistance in series, with a shunt capacitance representing electrode and stray capacitance
Motional capacitance, motional inductance, loss resistance, and a capacitor representing electrode and stray capacitance all in parallel
Motional capacitance, motional inductance, loss resistance, and a capacitor represent electrode and stray capacitance all in series
Motional inductance and loss resistance in series, paralleled with motional capacitance and a capacitor representing electrode and stray capacitance
E6F02: What happens to the conductivity of a photoconductive material when light shines on it?
It increases
It decreases
It stays the same
It becomes unstable
E7A15: What is a D flip-flop?
A flip-flop whose output takes on the state of the D input when the clock signal transitions from low to high
A differential class D amplifier used as a flip-flop circuit
A dynamic memory storage element
A flip-flop whose output is capable of both positive and negative voltage excursions
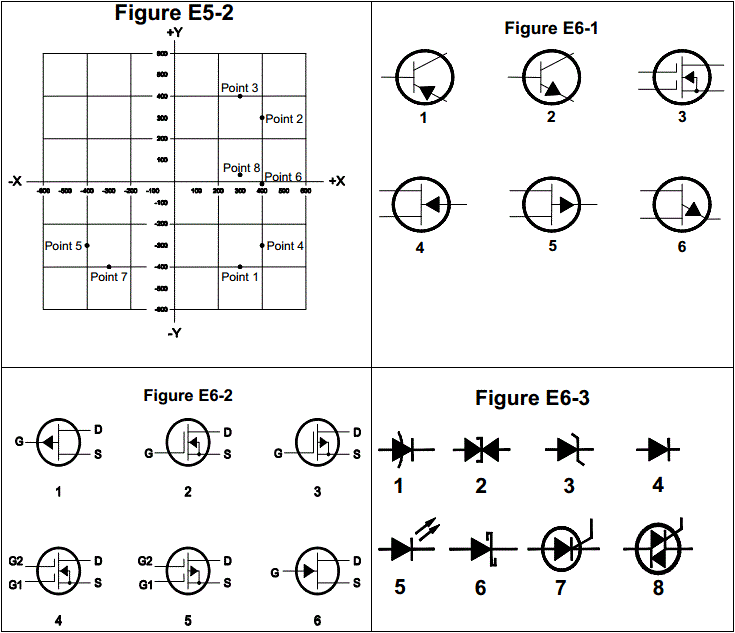
E7B13: In Figure E7-2, what is the purpose of R?
Emitter load
Fixed bias
Collector load
Voltage regulation
E7C14: Which of these modes is most affected by non-linear phase response in a receiver IF filter?
Meteor Scatter
Single-Sideband voice
Digital
Video
E7D14: What is one purpose of a "bleeder" resistor in a conventional (unregulated) power supply?
To cut down on waste heat generated by the power supply
To balance the low-voltage filament windings
To improve output voltage regulation
To boost the amount of output current
E7E05: What circuit is added to an FM transmitter to boost the higher audio frequencies?
A de-emphasis network
A heterodyne suppressor
An audio prescaler
A pre-emphasis network
E7F09: What is the purpose of a frequency counter?
To provide a digital representation of the frequency of a signal
To generate a series of reference signals at known frequency intervals
To display all frequency components of a transmitted signal
To provide a signal source at a very accurate frequency
E7G15: What is the typical output impedance of an integrated circuit op-amp?
Very low
Very high
100 ohms
1000 ohms
E7H08: What is a Gunn diode oscillator?
An oscillator based on the negative resistance properties of properly-doped semiconductors
An oscillator based on the argon gas diode
A highly stable reference oscillator based on the tee-notch principle
A highly stable reference oscillator based on the hot-carrier effect
E8A15: What would the waveform of a stream of digital data bits look like on a conventional oscilloscope?
A series of sine waves with evenly spaced gaps
A series of pulses with varying patterns
A running display of alpha-numeric characters
None of the above; this type of signal cannot be seen on a conventional oscilloscope
E8B07: When using a pulse-width modulation system, why is the transmitter's peak power greater than its average power?
The signal duty cycle is less than 100%
The signal reaches peak amplitude only when voice modulated
The signal reaches peak amplitude only when voltage spikes are generated within the modulator
The signal reaches peak amplitude only when the pulses are also amplitude modulated
E8C01: Which one of the following digital codes consists of elements having unequal length?
ASCII
AX.25
Baudot
Morse code
E8D09: What is meant by circularly polarized electromagnetic waves?
Waves with an electric field bent into a circular shape
Waves with a rotating electric field
Waves that circle the Earth
Waves produced by a loop antenna
E9A06: What is included in the total resistance of an antenna system?
Radiation resistance plus space impedance
Radiation resistance plus transmission resistance
Transmission-line resistance plus radiation resistance
Radiation resistance plus ohmic resistance
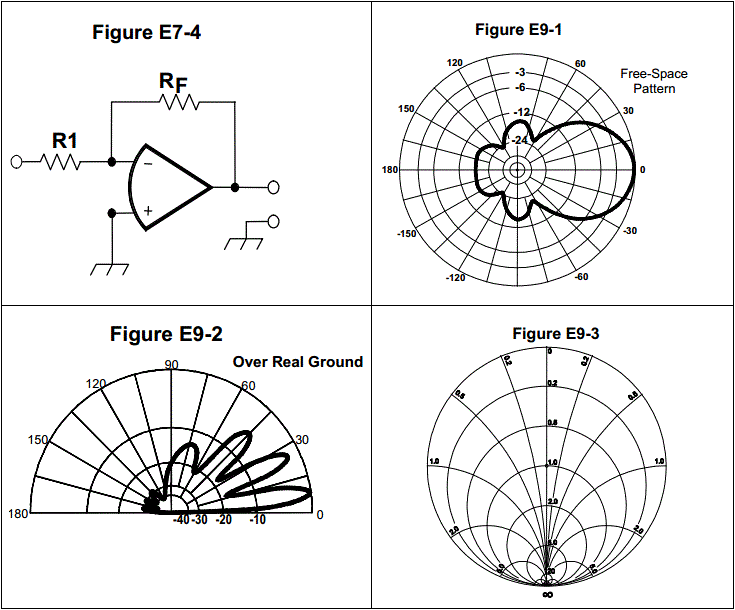
E9B03: In the antenna radiation pattern shown in Figure E9-1, what is the front-to-side ratio?
12 dB
14 dB
18 dB
24 dB
E9C10: How many elevation lobes appear in the forward direction of the antenna radiation pattern shown in Figure E9-2?
4
3
1
7
E9D05: Where should a high-Q loading coil be placed to minimize losses in a shortened vertical antenna?
Near the center of the vertical radiator
As low as possible on the vertical radiator
As close to the transmitter as possible
At a voltage node
E9E01: What system matches a high-impedance transmission line to a lower impedance antenna by connecting the line to the driven element in two places spaced a fraction of a wavelength each side of element center?
The gamma matching system
The delta matching system
The omega matching system
The stub matching system
E9F07: How does ladder line compare to small-diameter coaxial cable such as RG-58 at 50 MHz?
Lower loss
Higher SWR
Smaller reflection coefficient
Lower velocity factor
E9G11: How are the wavelength scales on a Smith chart calibrated?
In fractions of transmission line electrical frequency
In fractions of transmission line electrical wavelength
In fractions of antenna electrical wavelength
In fractions of antenna electrical frequency
E9H10: How can the output voltage of a multi-turn receiving loop antenna be increased?
By reducing the permeability of the loop shield
By increasing the number of wire turns in the loop and reducing the area of the loop structure
By winding adjacent turns in opposing directions
By increasing either the number of wire turns in the loop or the area of the loop structure or both