Ham General License Practice Quiz
• Percentage: 0%; Correct: 0; Total: 0 of 35
G0A05: What must you do if an evaluation of your station shows RF energy radiated from your station exceeds permissible limits?
Take action to prevent human exposure to the excessive RF fields
File an Environmental Impact Statement (EIS-97) with the FCC
Secure written permission from your neighbors to operate above the controlled MPE limits
All of these choices are correct
G0B02: What is the minimum wire size that may be safely used for a circuit that draws up to 20 amperes of continuous current?
AWG number 20
AWG number 16
AWG number 12
AWG number 8
G1A14: Which of the following applies when the FCC rules designate the Amateur Service as a secondary user on a band?
Amateur stations must record the call sign of the primary service station before operating on a frequency assigned to that station
Amateur stations are allowed to use the band only during emergencies
Amateur stations are allowed to use the band only if they do not cause harmful interference to primary users
Amateur stations may only operate during specific hours of the day, while primary users are permitted 24 hour use of the band
G1B09: When may an amateur station transmit communications in which the licensee or control operator has a pecuniary (monetary) interest?
When other amateurs are being notified of the sale of apparatus normally used in an amateur station and such activity is not done on a regular basis
Only when there is no other means of communications readily available
When other amateurs are being notified of the sale of any item with a monetary value less than $200 and such activity is not done on a regular basis
Never
G1C03: What is the maximum bandwidth permitted by FCC rules for Amateur Radio stations when transmitting on USB frequencies in the 60 meter band?
2.8 kHz
5.6 kHz
1.8 kHz
3 kHz
G1D01: Which of the following is a proper way to identify when transmitting using phone on General Class frequencies if you have a CSCE for the required elements but your upgrade from Technician has not appeared in the FCC database?
Give your call sign followed by the words "General Class"
No special identification is needed
Give your call sign followed by "slant AG"
Give your call sign followed the abbreviation 'CSCE'
G1E09: What language must you use when identifying your station if you are using a language other than English in making a contact using phone emission?
The language being used for the contact
Any language if the US has a third party agreement with that country
English
Any language of a country that is a member of the ITU
G2A05: Which mode of voice communication is most commonly used on the high frequency amateur bands?
Frequency modulation
Double sideband
Single sideband
Phase modulation
G2B02: What is the first thing you should do if you are communicating with another amateur station and hear a station in distress break in?
Continue your communication because you were on frequency first
Acknowledge the station in distress and determine what assistance may be needed
Change to a different frequency
Immediately cease all transmissions
G2C05: What is the best speed to use answering a CQ in Morse Code?
The fastest speed at which you are comfortable copying
The speed at which the CQ was sent
A slow speed until contact is established
5 wpm, as all operators licensed to operate CW can copy this speed
G2D07: Which of the following is required by the FCC rules when operating in the 60 meter band?
If you are using other than a dipole antenna, you must keep a record of the gain of your antenna
You must keep a log of the date, time, frequency, power level and stations worked
You must keep a log of all third party traffic
You must keep a log of the manufacturer of your equipment and the antenna used
G2E11: What does the abbreviation "MFSK" stand for?
Manual Frequency Shift Keying
Multi (or Multiple) Frequency Shift Keying
Manual Frequency Sideband Keying
Multi (or Multiple) Frequency Sideband Keying
G3A15: How long does it take charged particles from coronal mass ejections to affect radio-wave propagation on the Earth?
28 days
14 days
4 to 8 minutes
20 to 40 hours
G3B11: What happens to HF propagation when the Lowest Usable Frequency (LUF) exceeds the Maximum Usable Frequency (MUF)?
No HF radio frequency will support ordinary skywave communications over the path
HF communications over the path are enhanced
Double hop propagation along the path is more common
Propagation over the path on all HF frequencies is enhanced
G3C02: Where on the Earth do ionospheric layers reach their maximum height?
Where the Sun is overhead
Where the Sun is on the opposite side of the Earth
Where the Sun is rising
Where the Sun has just set
G4A09: Why is a time delay sometimes included in a transmitter keying circuit?
To prevent stations from talking over each other
To allow the transmitter power regulators to charge properly
To allow time for transmit-receive changeover operations to complete properly before RF output is allowed
To allow time for a warning signal to be sent to other stations
G4B01: What item of test equipment contains horizontal and vertical channel amplifiers?
An ohmmeter
A signal generator
An ammeter
An oscilloscope
G4C12: Which of the following is an advantage of a receiver Digital Signal Processor IF filter as compared to an analog filter?
A wide range of filter bandwidths and shapes can be created
Fewer digital components are required
Mixing products are greatly reduced
The DSP filter is much more effective at VHF frequencies
G4D09: What frequency range is occupied by a 3 kHz USB signal with the displayed carrier frequency set to 14.347 MHz?
14.347 to 14.647 MHz
14.347 to 14.350 MHz
14.344 to 14.347 MHz
14.3455 to 14.3485 MHz
G4E01: What is a "capacitance hat", when referring to a mobile antenna?
A device to increase the power handling capacity of a mobile whip antenna
A device that allows automatic band-changing for a mobile antenna
A device to electrically lengthen a physically short antenna
A device that allows remote tuning of a mobile antenna
G5A08: Why is impedance matching important?
So the source can deliver maximum power to the load
So the load will draw minimum power from the source
To ensure that there is less resistance than reactance in the circuit
To ensure that the resistance and reactance in the circuit are equal
G5B03: How many watts of electrical power are used if 400 VDC is supplied to an 800-ohm load?
0.5 watts
200 watts
400 watts
3200 watts
G5C13: Which of the following components should be added to a capacitor to increase the capacitance?
An inductor in series
A resistor in series
A capacitor in parallel
A capacitor in series
G6A11: Why would it be important to minimize the mutual inductance between two inductors?
To increase the energy transfer between circuits
To reduce unwanted coupling between circuits
To reduce conducted emissions
To increase the self-resonant frequency of the inductors
G6B04: When two or more diodes are connected in parallel to increase current handling capacity, what is the purpose of the resistor connected in series with each diode?
To ensure the thermal stability of the power supply
To regulate the power supply output voltage
To ensure that one diode doesn't carry most of the current
To act as an inductor
G6C09: Which of the following is a characteristic of a liquid crystal display?
It requires ambient or back lighting
It offers a wide dynamic range
It has a wide viewing angle
All of these choices are correct
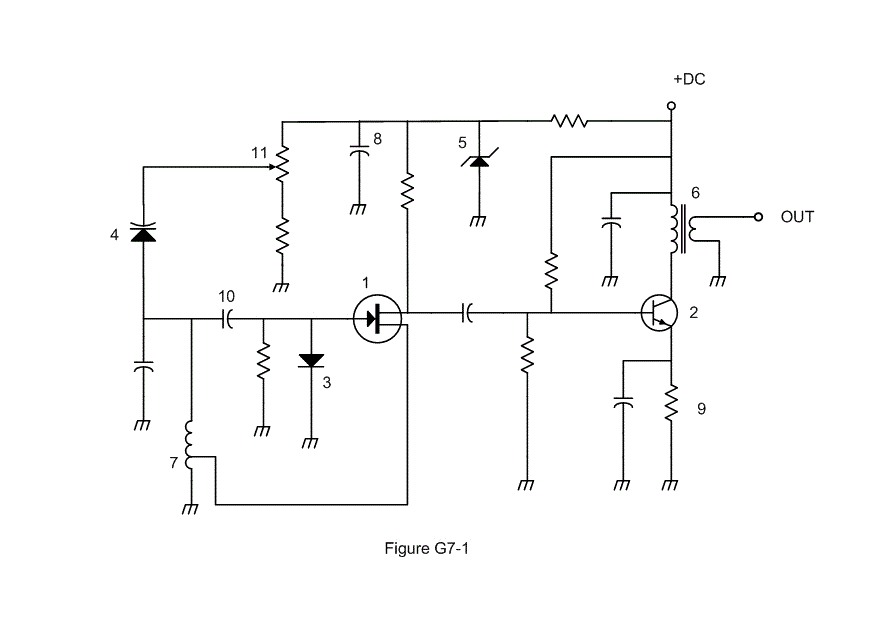
G7A09: Which symbol in figure G7-1 represents a field effect transistor?
Symbol 2
Symbol 5
Symbol 1
Symbol 4
G7B11: For which of the following modes is a Class C power stage appropriate for amplifying a modulated signal?
SSB
CW
AM
All of these choices are correct
G7C09: Which of the following is needed for a Digital Signal Processor IF filter?
An analog to digital converter
A digital to analog converter
A digital processor chip
All of the these choices are correct
G8A09: What control is typically adjusted for proper ALC setting on an amateur single sideband transceiver?
The RF clipping level
Transmit audio or microphone gain
Antenna inductance or capacitance
Attenuator level
G8B08: Why is it important to know the duty cycle of the data mode you are using when transmitting?
To aid in tuning your transmitter
Some modes have high duty cycles which could exceed the transmitter's average power rating.
To allow time for the other station to break in during a transmission
All of these choices are correct
G9A11: What standing wave ratio will result from the connection of a 50-ohm feed line to a non-reactive load having a 50-ohm impedance?
2:1
1:1
50:50
0:0
G9B01: What is one disadvantage of a directly fed random-wire antenna?
It must be longer than 1 wavelength
You may experience RF burns when touching metal objects in your station
It produces only vertically polarized radiation
It is not effective on the higher HF bands
G9C08: What is meant by the "main lobe" of a directive antenna?
The magnitude of the maximum vertical angle of radiation
The point of maximum current in a radiating antenna element
The maximum voltage standing wave point on a radiating element
The direction of maximum radiated field strength from the antenna
G9D03: At what height above ground is an NVIS antenna typically installed?
As close to one-half wave as possible
As close to one wavelength as possible
Height is not critical as long as it is significantly more than 1/2 wavelength
Between 1/10 and 1/4 wavelength