Ham Extra License Practice Quiz
• Percentage: 0%; Correct: 0; Total: 0 of 50
E0A06: Why are there separate electric (E) and magnetic (H) field MPE limits?
The body reacts to electromagnetic radiation from both the E and H fields
Ground reflections and scattering make the field impedance vary with location
E field and H field radiation intensity peaks can occur at different locations
All of these choices are correct
E1A13: Who must be in physical control of the station apparatus of an amateur station aboard any vessel or craft that is documented or registered in the United States?
Only a person with an FCC Marine Radio
Any person holding an FCC-issued amateur license or who is authorized for alien reciprocal operation
Only a person named in an amateur station license grant
Any person named in an amateur station license grant or a person holding an unrestricted Radiotelephone Operator Permit
E1B06: Which of the following additional rules apply if you are installing an amateur station antenna at a site at or near a public use airport?
You may have to notify the Federal Aviation Administration and register it with the FCC as required by Part 17 of FCC rules
No special rules apply if your antenna structure will be less than 300 feet in height
You must file an Environmental Impact Statement with the EPA before construction begins
You must obtain a construction permit from the airport zoning authority
E1C04: When may an automatically controlled station retransmit third party communications?
Never
Only when transmitting RTTY or data emissions
When specifically agreed upon by the sending and receiving stations
When approved by the National Telecommunication and Information Administration
E1D06: Which of the following special provisions must a space station incorporate in order to comply with space station requirements?
The space station must be capable of terminating transmissions by telecommand when directed by the FCC
The space station must cease all transmissions after 5 years
The space station must be capable of changing its orbit whenever such a change is ordered by NASA
All of these choices are correct
E1E12: What must the VE team do with the application form if the examinee does not pass the exam?
Return the application document to the examinee
Maintain the application form with the VEC's records
Send the application form to the FCC and inform the FCC of the grade
Destroy the application form
E1F11: Which of the following best describes one of the standards that must be met by an external RF power amplifier if it is to qualify for a grant of FCC certification?
It must produce full legal output when driven by not more than 5 watts of mean RF input power
It must be capable of external RF switching between its input and output networks
It must exhibit a gain of 0 dB or less over its full output range
It must satisfy the FCC's spurious emission standards when operated at the lesser of 1500 watts, or its full output power
E2A03: What is the orbital period of an Earth satellite?
The point of maximum height of a satellite's orbit
The point of minimum height of a satellite's orbit
The time it takes for a satellite to complete one revolution around the Earth
The time it takes for a satellite to travel from perigee to apogee
E2B12: How are analog SSTV images typically transmitted on the HF bands?
Video is converted to equivalent Baudot representation
Video is converted to equivalent ASCII representation
Varying tone frequencies representing the video are transmitted using PSK
Varying tone frequencies representing the video are transmitted using single sideband
E2C04: On which of the following frequencies is an amateur radio contest contact generally discouraged?
3.525 MHz
14.020 MHz
28.330 MHz
146.52 MHz
E2D01: Which of the following digital modes is especially designed for use for meteor scatter signals?
WSPR
FSK441
Hellschreiber
APRS
E2E03: How is Forward Error Correction implemented?
By the receiving station repeating each block of three data characters
By transmitting a special algorithm to the receiving station along with the data characters
By transmitting extra data that may be used to detect and correct transmission errors
By varying the frequency shift of the transmitted signal according to a predefined algorithm
E3A03: When scheduling EME contacts, which of these conditions will generally result in the least path loss?
When the Moon is at perigee
When the Moon is full
When the Moon is at apogee
When the MUF is above 30 MHz
E3B06: Which of the following amateur bands most frequently provides long-path propagation?
80 meters
20 meters
10 meters
6 meters
E3C05: Which of the following describes selective fading?
Variability of signal strength with beam heading
Partial cancellation of some frequencies within the received pass band
Sideband inversion within the ionosphere
Degradation of signal strength due to backscatter
E4A04: Which of the following test instruments is used to display spurious signals from a radio transmitter?
A spectrum analyzer
A wattmeter
A logic analyzer
A time-domain reflectometer
E4B14: What happens if a dip meter is too tightly coupled to a tuned circuit being checked?
Harmonics are generated
A less accurate reading results
Cross modulation occurs
Intermodulation distortion occurs
E4C12: What is an undesirable effect of using too wide a filter bandwidth in the IF section of a receiver?
Output-offset overshoot
Filter ringing
Thermal-noise distortion
Undesired signals may be heard
E4D06: What is the term for unwanted signals generated by the mixing of two or more signals?
Amplifier desensitization
Neutralization
Adjacent channel interference
Intermodulation interference
E4E13: What might be the cause of a loud roaring or buzzing AC line interference that comes and goes at intervals?
Arcing contacts in a thermostatically controlled device
A defective doorbell or doorbell transformer inside a nearby residence
A malfunctioning illuminated advertising display
All of these choices are correct
E5A08: What is the phase relationship between the current through and the voltage across a series resonant circuit at resonance?
The voltage leads the current by 90 degrees
The current leads the voltage by 90 degrees
The voltage and current are in phase
The voltage and current are 180 degrees out of phase
E5B10: What is the relationship between the current through an inductor and the voltage across an inductor?
Voltage leads current by 90 degrees
Current leads voltage by 90 degrees
Voltage and current are 180 degrees out of phase
Voltage and current are in phase
E5C01: In polar coordinates, what is the impedance of a network consisting of a 100-ohm-reactance inductor in series with a 100-ohm resistor?
121 ohms at an angle of 35 degrees
141 ohms at an angle of 45 degrees
161 ohms at an angle of 55 degrees
181 ohms at an angle of 65 degrees
E5D05: Which of the following creates a magnetic field?
Potential differences between two points in space
Electric current
A charged capacitor
A battery
E6A04: What is the name given to an impurity atom that adds holes to a semiconductor crystal structure?
Insulator impurity
N-type impurity
Acceptor impurity
Donor impurity
E6B13: What type of bias is required for an LED to emit light?
Reverse bias
Forward bias
Zero bias
Inductive bias
E6C03: Which of the following describes tri-state logic?
Logic devices with 0, 1, and high impedance output states
Logic devices that utilize ternary math
Low power logic devices designed to operate at 3 volts
Proprietary logic devices manufactured by Tri-State Devices
E6D09: What devices are commonly used as VHF and UHF parasitic suppressors at the input and output terminals of transistorized HF amplifiers?
Electrolytic capacitors
Butterworth filters
Ferrite beads
Steel-core toroids
E6E04: What is the most common input and output impedance of circuits that use MMICs?
50 ohms
300 ohms
450 ohms
10 ohms
E6F03: What is the most common configuration of an optoisolator or optocoupler?
A lens and a photomultiplier
A frequency modulated helium-neon laser
An amplitude modulated helium-neon laser
An LED and a phototransistor
E7A03: Which of the following can divide the frequency of a pulse train by 2?
An XOR gate
A flip-flop
An OR gate
A multiplexer
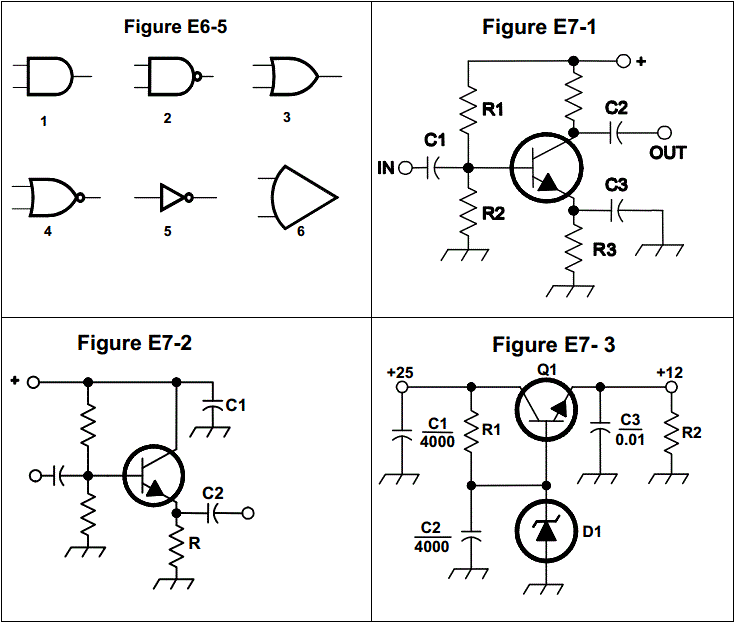
E7B13: In Figure E7-2, what is the purpose of R?
Emitter load
Fixed bias
Collector load
Voltage regulation
E7C03: What advantage does a Pi-L-network have over a Pi-network for impedance matching between the final amplifier of a vacuum-tube transmitter and an antenna?
Greater harmonic suppression
Higher efficiency
Lower losses
Greater transformation range
E7D09: What is the purpose of C1 in the circuit shown in Figure E7-3?
It resonates at the ripple frequency
It provides fixed bias for Q1
It decouples the output
It filters the supply voltage
E7E04: What is one way a single-sideband phone signal can be generated?
By using a balanced modulator followed by a filter
By using a reactance modulator followed by a mixer
By using a loop modulator followed by a mixer
By driving a product detector with a DSB signal
E7F06: What is one purpose of a marker generator?
To add audio markers to an oscilloscope
To provide a frequency reference for a phase locked loop
To provide a means of calibrating a receiver's frequency settings
To add time signals to a transmitted signal
E7G15: What is the typical output impedance of an integrated circuit op-amp?
Very low
Very high
100 ohms
1000 ohms
E7H11: What are the major spectral impurity components of direct digital synthesizers?
Broadband noise
Digital conversion noise
Spurious signals at discrete frequencies
Nyquist limit noise
E8A11: What is one use for a pulse modulated signal?
Linear amplification
PSK31 data transmission
Multiphase power transmission
Digital data transmission
E8B03: What is the modulation index of an FM-phone signal having a maximum frequency deviation of 3000 Hz either side of the carrier frequency, when the modulating frequency is 1000 Hz?
3
0.3
3000
1000
E8C01: Which one of the following digital codes consists of elements having unequal length?
ASCII
AX.25
Baudot
Morse code
E8D15: Which of the following is a typical value for the RMS voltage at a standard U.S. household electrical power outlet?
120V AC
340V AC
85V AC
170V AC
E9A08: What is meant by antenna gain?
The ratio relating the radiated signal strength of an antenna in the direction of maximum radiation to that of a reference antenna
The ratio of the signal in the forward direction to that in the opposite direction
The ratio of the amount of power radiated by an antenna compared to the transmitter output power
The final amplifier gain minus the transmission-line losses, including any phasing lines present
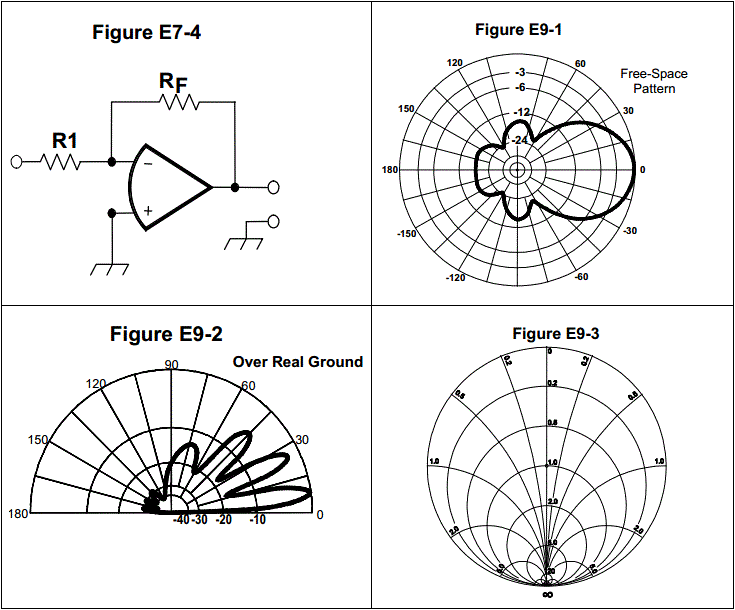
E9B03: In the antenna radiation pattern shown in Figure E9-1, what is the front-to-side ratio?
12 dB
14 dB
18 dB
24 dB
E9C09: What is the front-to-back ratio of the radiation pattern shown in Figure E9-2?
15 dB
28 dB
3 dB
24 dB
E9D02: How can linearly polarized Yagi antennas be used to produce circular polarization?
Stack two Yagis, fed 90 degrees out of phase, to form an array with the respective elements in parallel planes
Stack two Yagis, fed in phase, to form an array with the respective elements in parallel planes
Arrange two Yagis perpendicular to each other with the driven elements at the same point on the boom and fed 90 degrees out of phase
Arrange two Yagis collinear to each other, with the driven elements fed 180 degrees out of phase
E9E03: What is the name of the matching system that uses a section of transmission line connected in parallel with the feed line at the feed point?
The gamma match
The delta match
The omega match
The stub match
E9F11: What impedance does a 1/8-wavelength transmission line present to a generator when the line is open at the far end?
The same as the characteristic impedance of the line
An inductive reactance
A capacitive reactance
The same as the input impedance of the final generator stage
E9G08: What is the process of normalization with regard to a Smith chart?
Reassigning resistance values with regard to the reactance axis
Reassigning reactance values with regard to the resistance axis
Reassigning impedance values with regard to the prime center
Reassigning prime center with regard to the reactance axis
E9H07: Why is it advisable to use an RF attenuator on a receiver being used for direction finding?
It narrows the bandwidth of the received signal to improve signal to noise ratio
It compensates for the effects of an isotropic antenna, thereby improving directivity
It reduces loss of received signals caused by antenna pattern nulls, thereby increasing sensitivity
It prevents receiver overload which could make it difficult to determine peaks or nulls