Ham General License Practice Quiz
• Percentage: 0%; Correct: 0; Total: 0 of 35
G0A01: What is one way that RF energy can affect human body tissue?
It heats body tissue
It causes radiation poisoning
It causes the blood count to reach a dangerously low level
It cools body tissue
G0B14: Which of the following is covered by the National Electrical Code?
Acceptable bandwidth limits
Acceptable modulation limits
Electrical safety inside the ham shack
RF exposure limits of the human body
G1A04: Which of the following amateur bands is restricted to communication on only specific channels, rather than frequency ranges?
11 meters
12 meters
30 meters
60 meters
G1B03: Which of the following is a purpose of a beacon station as identified in the FCC Rules?
Observation of propagation and reception
Automatic identification of repeaters
Transmission of bulletins of general interest to Amateur Radio licensees
Identifying net frequencies
G1C11: What is the maximum symbol rate permitted for RTTY or data emission transmissions on the 2 meter band?
56 kilobaud
19.6 kilobaud
1200 baud
300 baud
G1D07: Volunteer Examiners are accredited by what organization?
The Federal Communications Commission
The Universal Licensing System
A Volunteer Examiner Coordinator
The Wireless Telecommunications Bureau
G1E09: What language must you use when identifying your station if you are using a language other than English in making a contact using phone emission?
The language being used for the contact
Any language if the US has a third party agreement with that country
English
Any language of a country that is a member of the ITU
G2A06: Which of the following is an advantage when using single sideband as compared to other analog voice modes on the HF amateur bands?
Very high fidelity voice modulation
Less bandwidth used and higher power efficiency
Ease of tuning on receive and immunity to impulse noise
Less subject to static crashes (atmospherics)
G2B01: Which of the following is true concerning access to frequencies?
Nets always have priority
QSO's in process always have priority
No one has priority access to frequencies, common courtesy should be a guide
Contest operations must always yield to non-contest use of frequencies
G2C07: When sending CW, what does a 'C' mean when added to the RST report?
Chirpy or unstable signal
Report was read from S meter reading rather than estimated
100 percent copy
Key clicks
G2D05: When is it permissible to communicate with amateur stations in countries outside the areas administered by the Federal Communications Commission?
Only when the foreign country has a formal third party agreement filed with the FCC
When the contact is with amateurs in any country except those whose administrations have notified the ITU that they object to such communications
When the contact is with amateurs in any country as long as the communication is conducted in English
Only when the foreign country is a member of the International Amateur Radio Union
G2E10: What is a major advantage of MFSK16 compared to other digital modes?
It is much higher speed than RTTY
It is much narrower bandwidth than most digital modes
It has built-in error correction
It offers good performance in weak signal environments without error correction
G3A07: At what point in the solar cycle does the 20 meter band usually support worldwide propagation during daylight hours?
At the summer solstice
Only at the maximum point of the solar cycle
Only at the minimum point of the solar cycle
At any point in the solar cycle
G3B02: Which of the following is a good indicator of the possibility of sky-wave propagation on the 6 meter band?
Short skip sky-wave propagation on the 10 meter band
Long skip sky-wave propagation on the 10 meter band
Severe attenuation of signals on the 10 meter band
Long delayed echoes on the 10 meter band
G3C01: Which of the following ionospheric layers is closest to the surface of the Earth?
The D layer
The E layer
The F1 layer
The F2 layer
G4A10: What is the purpose of an electronic keyer?
Automatic transmit/receive switching
Automatic generation of strings of dots and dashes for CW operation
VOX operation
Computer interface for PSK and RTTY operation
G4B05: Why is high input impedance desirable for a voltmeter?
It improves the frequency response
It decreases battery consumption in the meter
It improves the resolution of the readings
It decreases the loading on circuits being measured
G4C09: How can a ground loop be avoided?
Connect all ground conductors in series
Connect the AC neutral conductor to the ground wire
Avoid using lock washers and star washers when making ground connections
Connect all ground conductors to a single point
G4D04: What does an S meter measure?
Conductance
Impedance
Received signal strength
Transmitter power output
G4E08: What is the name of the process by which sunlight is changed directly into electricity?
Photovoltaic conversion
Photon emission
Photosynthesis
Photon decomposition
G5A06: How does a capacitor react to AC?
As the frequency of the applied AC increases, the reactance decreases
As the frequency of the applied AC increases, the reactance increases
As the amplitude of the applied AC increases, the reactance increases
As the amplitude of the applied AC increases, the reactance decreases
G5B11: What is the ratio of peak envelope power to average power for an unmodulated carrier?
.707
1.00
1.414
2.00
G5C04: What is the total resistance of three 100-ohm resistors in parallel?
.30 ohms
.33 ohms
33.3 ohms
300 ohms
G6A12: What is a common name for an inductor used to help smooth the DC output from the rectifier in a conventional power supply?
Back EMF choke
Repulsion coil
Charging inductor
Filter choke
G6B06: Which of the following is an advantage of using a Schottky diode in an RF switching circuit as compared to a standard silicon diode?
Lower capacitance
Lower inductance
Longer switching times
Higher breakdown voltage
G6C06: Which of the following describes an integrated circuit operational amplifier?
Digital
MMIC
Programmable Logic
Analog
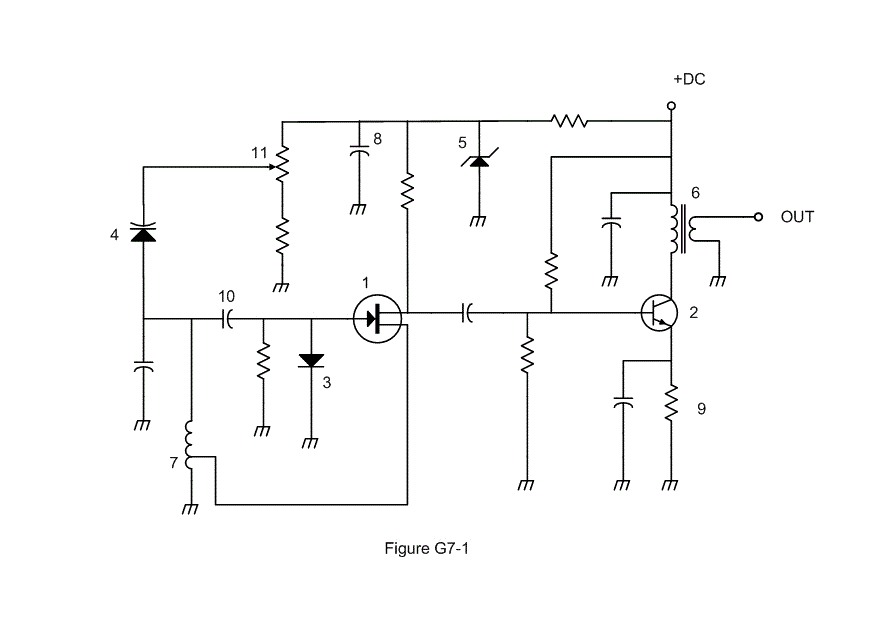
G7A11: Which symbol in figure G7-1 represents an NPN junction transistor?
Symbol 1
Symbol 2
Symbol 7
Symbol 11
G7B14: Which of the following describes a linear amplifier?
Any RF power amplifier used in conjunction with an amateur transceiver
An amplifier in which the output preserves the input waveform
A Class C high efficiency amplifier
An amplifier used as a frequency multiplier
G7C10: How is Digital Signal Processor filtering accomplished?
By using direct signal phasing
By converting the signal from analog to digital and using digital processing
By differential spurious phasing
By converting the signal from digital to analog and taking the difference of mixing products
G8A02: What is the name of the process that changes the phase angle of an RF wave to convey information?
Phase convolution
Phase modulation
Angle convolution
Radian inversion
G8B04: What is the name of the stage in a VHF FM transmitter that generates a harmonic of a lower frequency signal to reach the desired operating frequency?
Mixer
Reactance modulator
Pre-emphasis network
Multiplier
G9A05: How does the attenuation of coaxial cable change as the frequency of the signal it is carrying increases?
It is independent of frequency
It increases
It decreases
It reaches a maximum at approximately 18 MHz
G9B06: Where should the radial wires of a ground-mounted vertical antenna system be placed?
As high as possible above the ground
Parallel to the antenna element
On the surface or buried a few inches below the ground
At the top of the antenna
G9C09: What is the approximate maximum theoretical forward gain of a three element, single-band Yagi antenna?
9.7 dBi
9.7 dBd
5.4 times the gain of a dipole
All of these choices are correct
G9D06: Which of the following is an advantage of a log periodic antenna?
Wide bandwidth
Higher gain per element than a Yagi antenna
Harmonic suppression
Polarization diversity